https://nesslabs.com/decision-making
We make thousands of choices everyday, often automatically, using mental models we have created over years of experience.
Modelos mentais: estão modelados na ROT
Decision-making is the process we use to identify and choose alternatives, producing a final choice, which may or may not result in an action. It can be more or less rational based on the decision maker’s values, beliefs, and (perceived) knowledge.
Decidir não agir é uma decisão também.
What’s interesting is that these areas are not only involved in the formation of a decision, but also signal the degree of confidence associated with the decision.
Grau de Confiança e Grau de Risco das decisões
In fact, poor decision-making rarely has to do with a lack of intelligence or information. Instead, we it’s often due to the ‘mental baggage’ we bring to the table when considering our options.
Pobres em que sentido?
Analysis paralysis. You may know this one under the term “overthinking.” You basically tend to spend so much time analysing all the possible outcomes that you never end up making a decision — which, often, is a bad decision in itself.
Análise das opções (mesmo que poucas) com muitos critérios
Information overload. We usually use information at our disposal to reduce uncertainty and make what we think our sound decisions. But sometimes, there’s more information that we can actually process. This can result in the illusion of knowledge and poor decision-making.
Mais difícil decidir quando tem muitas opções
Intuitive vs. rational. Your decision-making is the result of a fight between two kinds of cognitive processes. The first, called System 1, is an automatic intuitive system. The second (you guessed it, System 2), is an effortful rational system. System 1 is fast, implicit, and bottom-up, while system 2 is slow, explicit, and top-down. You can read more about it in the excellent book Thinking, Fast and Slow by psychologist Daniel Kahneman.
Dica de Livro interessante
Maximising vs. satisficing. People tend to fall under two main cognitive styles. Maximisers try to make an optimal decision, whereas satisficers simply try to find a solution that is good enough. As a result, maximisers usually take longer to make a decision, thinking carefully about the potential outcomes and corresponding tradeoffs. They will also tend to regret their decisions more often.
O ótimo é inimigo do bom!!! Demorar para decidir pode fazer a decisão perder o efeito pela mudança do cenário.
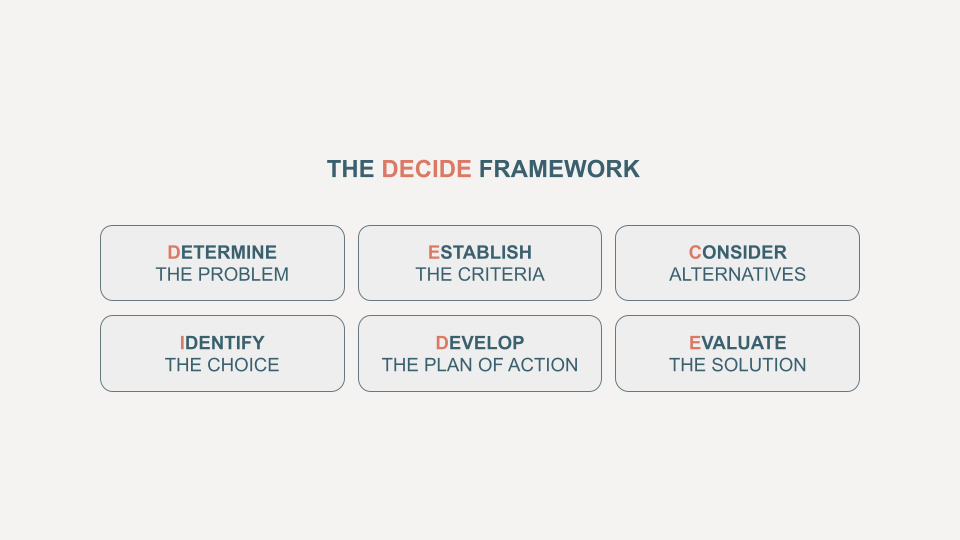
To put it simply, mental models are a set of beliefs and ideas that we consciously or unconsciously form based on our experiences. They guide our thoughts and behaviours and help us understand life. They’re basically thinking tools—shortcuts for reasoning.
Comentários
Postar um comentário
Sinta-se a vontade para comentar. Críticas construtivas são sempre bem vindas.