https://kgtk.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
KGTK represents KGs using TSV files with 4 columns labeled id, node1, label and node2. The id column is a symbol representing an identifier of an edge, corresponding to the orange circles in the diagram above. node1 represents the source of the edge, node2 represents the destination of the edge, and label represents the relation between node1 and node2.
>> Quad do RDF, definir cada tripla como um grafo
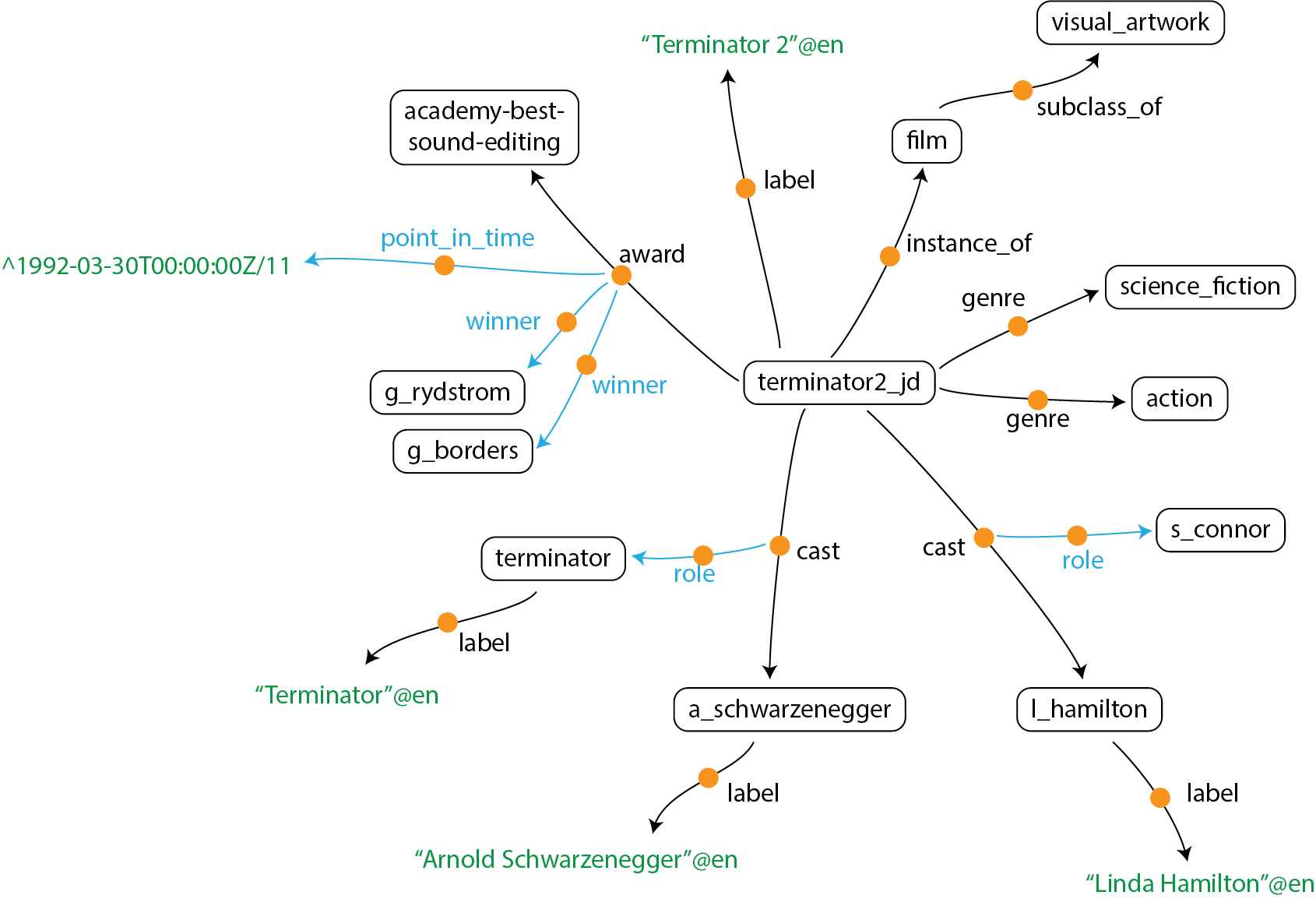
KGTK defines knowledge graphs (or more generally any attributed graph or hypergraph) as a set of nodes and a set of edges between those nodes. KGTK represents everything of meaning via an edge. Edges themselves can be attributed by having edges asserted about them, thus, KGTK can in fact represent arbitrary hypergraphs. KGTK intentionally does not distinguish attributes or qualifiers on nodes and edges from full-fledged edges, tools operating on KGTK graphs can instead interpret edges differently if they so desire. In KGTK, everything can be a node, and every node can have any type of edge to any other node.
import-ntriples: This command will import one or more ntriple files into KGTK format.
>> Existem comando de importação para KGs como Wikidata
The generate-wikidata-triples command generates triple files from a kgtk file. The generated triple files can then be loaded into a triple store directly.
The triple generator reads a tab-separated kgtk file from standard input, by default, or a given file. The kgtk file is required to have at least the following 4 fields: node1, label, node2 and id. The node1 field is the subject; label is the predicate and node2 is the object.
>> Converter Wikidata em RDF para carregar em TripleStore
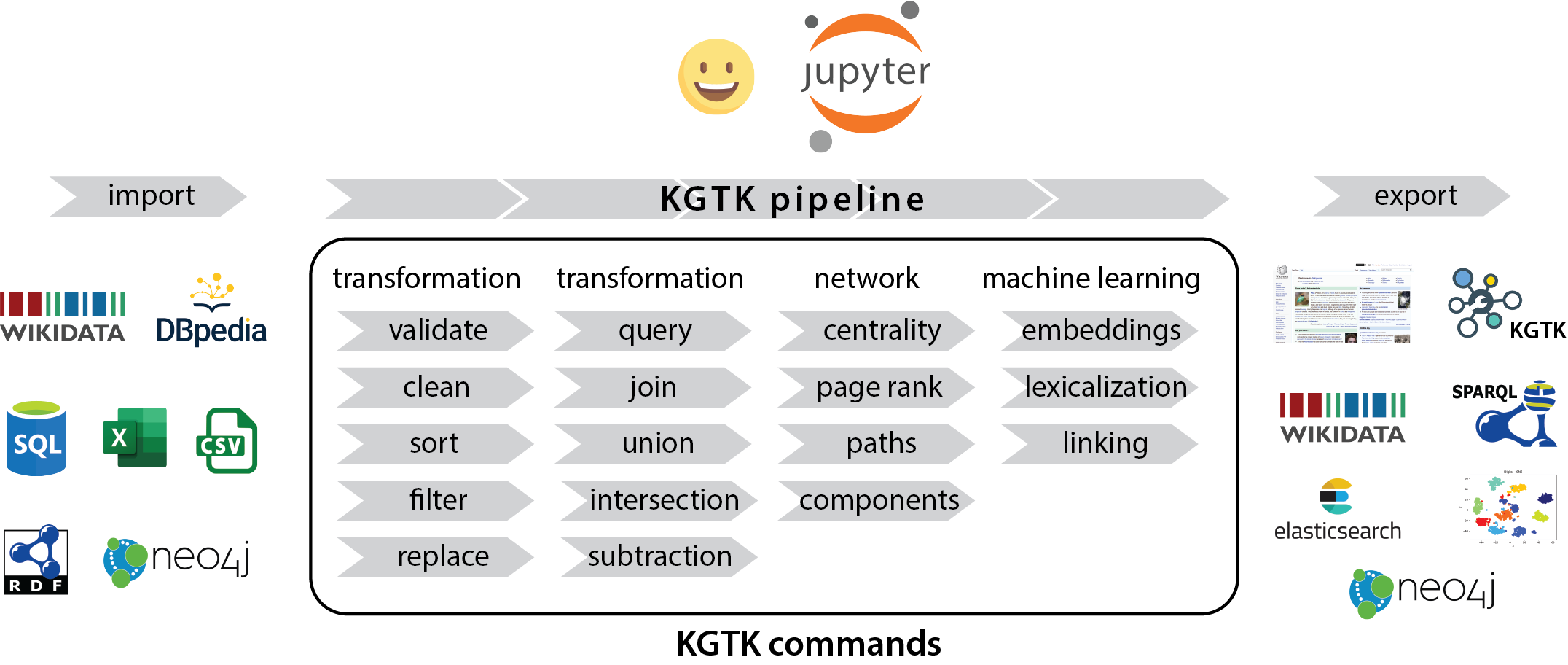
Transformation commands
calc: this command performs calculations on one or more columns in a KGTK file. The output of a calculation can be written into an existing column or into a new column, which will be added after all existing columns.
lexicalize builds English sentences from KGTK edge files. The primary purpose of this command is to construct inputs for text-based distance vector analysis. However, it may also prove useful for explaining the contents of local subsets of Knowledge Graphs.
Curation commands
validate-properties validates and filter property patterns in a KGTK file. We want to be able to detect violations of various constraint patterns.
An existing system, SHACL, is an RDF-based constraint system. We'd like KGTK to have something that is both easier for new users than RDF and more efficient to run.
Analysis
find the connected components in a KGTK edge file.
compute the the embeddings of this files' entities. We are using structure of nodes and their relations to compute embeddings of nodes. The set of metrics to compute are specified by the user. There are three supported formats: glove, w2v, and kgtk. The algorithm by default is ComplEx (also supports TransE, DistMult, or RESCAL)
compute centrality metrics and connectivity statistics.
computes paths between each pair of source-target nodes
find all nodes reachable from given root nodes in a KGTK edge file. That is, given a set of nodes N and a set of properties P, this command computes the set of nodes R that can be reached from N via paths containing any of the properties in P.
Computes embeddings of nodes using properties of nodes. The values are concatenated into sentences defined by a template, and embedded using a pre-trained language model.
Artigo -> https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.00088.pdf
KGTK não é hiper grafo.
ResponderExcluir