Um série de 3 artigos de abrilde2019 que cobrem as 3 camadas
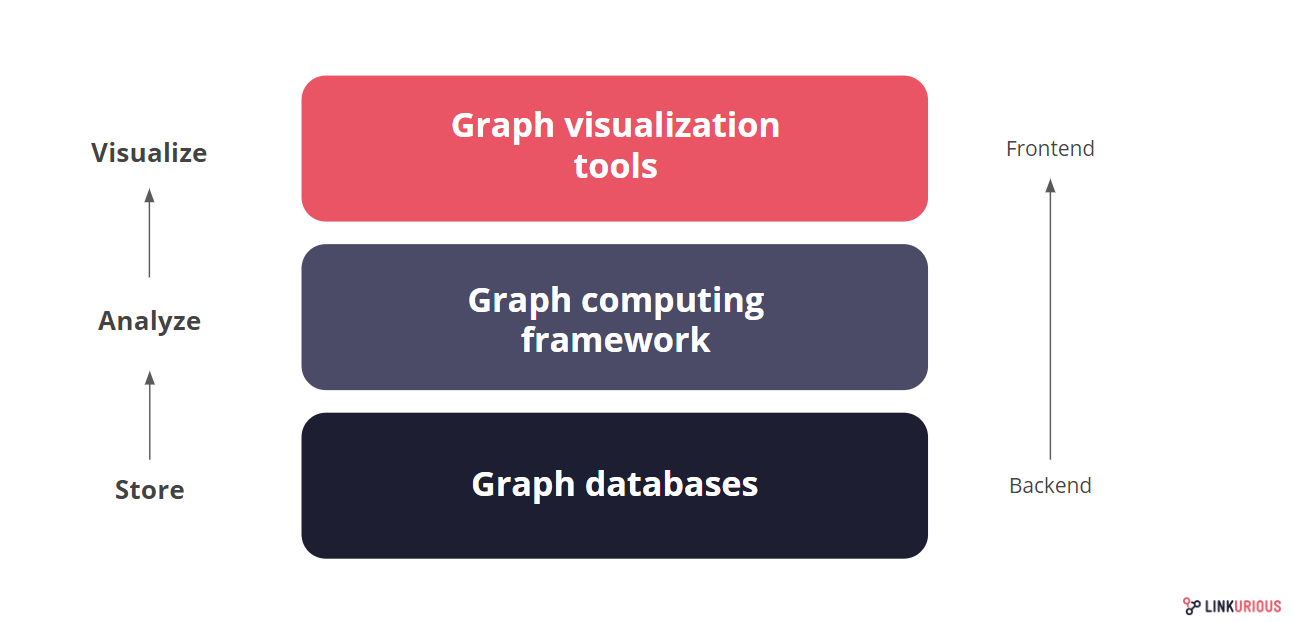
Cada Graph Database presente nessa imagem é apresentado entre o slide 5 e o 81 da apresentação que consta no final do artigo.


Cada tecnologia da camada de Analytics presente na próxima imagem consta na apresentação do final do artigo.
- Graph processing frameworks / engines (slide 5 ao 26)
- Graph analytics libraries and toolkits (slide 28 ao 46)
- Query languages (slide 48 ao 64)

Giraph, GraphX (Apache Spark), Faunus (Hadoop)

Gephi, Cytospace

Alguns Graph Databases possuem visualizadores como o Neo4J e o Allegro (Gruff)
Os artigos são atualizações de um artigo originalmente publicado (2014) em https://linkurio.us/blog/introduction-graph-technologies-landscape/
Um importante insight do último artigo que me lembrou o comentário que o professor Villas fez sobre o Busc@NIMA:
Visualization tools represent an important bridge between graph data and analysts. It helps surface information and insights leading to the understanding of a situation, or the solving of a problem.
While it’s easy to read and comprehend non-graph data in a tabular format such as a spreadsheet, you will probably miss valuable information if you try to analyze connected data the same way.
Representing connected data in tables is not intuitive and often hides the connections in which lies the value.
Graph visualization tools turn connected data into graphical network representations that takes advantage of the human brain proficiency to recognize visual patterns and more pattern variations.
Comentários
Postar um comentário
Sinta-se a vontade para comentar. Críticas construtivas são sempre bem vindas.